SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT WITH US
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic specialist for a detailed consultation & personalised treatment plan today.
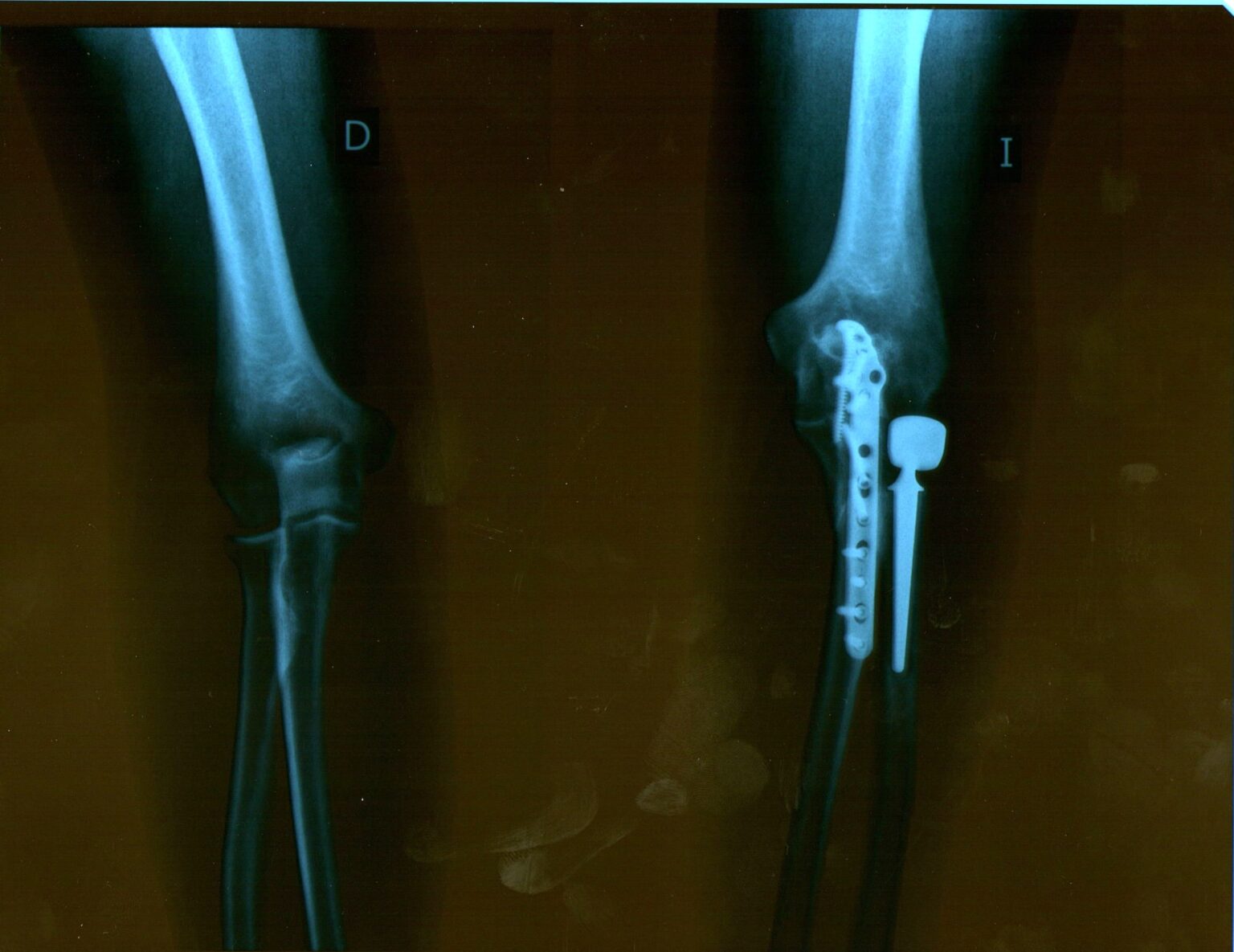
ORIF (Open Reduction and Internal Fixation) is a surgical procedure used to repair complex fractures around the knee joint.
In this procedure, the bone is first realigned (open reduction), and then metal plates, screws, or rods are used to hold the bone in place (internal fixation) as it heals. ORIF surgery is typically used for fractures that cannot heal properly with non-surgical treatment, such as casting or splinting, and is required to restore knee stability and function.
ORIF surgery is indicated when non-surgical treatments are insufficient to heal the knee fracture and is recommended for the following conditions:
ORIF is recommended for fractures with multiple breaks or displaced bone fragments, which makes healing difficult without surgical intervention.
Fractures that extend into the knee joint itself may require ORIF surgery to realign the bones and preserve joint function, reducing the risk of long-term complications like arthritis.
When a knee fracture causes instability and the bones cannot remain in place without support, ORIF surgery is needed to stabilise the knee during the healing process.
Fractures that have not healed correctly with non-surgical methods like casting or bracing may require ORIF surgery to ensure proper bone alignment and healing. This is often seen in cases where fractures are complex, displaced, or located in critical areas of the knee joint.
ORIF surgery provides several advantages for patients with complex knee fractures, which include the following:
The type of ORIF surgery varies depending on the location and type of fracture.
This procedure is used for fractures of the patella (kneecap). The surgeon uses metal pins or screws to reattach the bone fragments and stabilise the kneecap.
Tibial plateau fractures occur at the top of the tibia (shinbone) near the knee joint. ORIF for tibial plateau fractures involves placing plates and screws to hold the bone fragments together and restore knee stability.
This procedure addresses fractures of the distal femur, the lower part of the thigh bone. Metal plates and screws are used to stabilise the femur and ensure proper healing.
Several steps are necessary before ORIF surgery to ensure a smooth procedure and reduce the risk of complications.
General or spinal anaesthesia is administered to ensure the patient is pain-free during the procedure. The type of anaesthesia depends on the fracture location and patient health.
The surgeon makes an incision near the knee to access the fractured bone. The bone fragments are then realigned (open reduction) to restore their proper position.
Metal plates, screws, or rods are inserted to hold the bone fragments in place while they heal (internal fixation). These devices remain in the body unless they cause discomfort and require removal later.
The incision is closed with stitches or staples, and the knee is bandaged. The internal fixation devices ensure that the bone stays aligned during the healing process.
SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT WITH US
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic specialist for a detailed consultation & personalised treatment plan today.
After ORIF surgery, proper post-operative care ensures successful healing and restored knee function.
While most patients recover well, ORIF surgery carries some potential risks and complications. The most common include:
Monday – Friday: 9.00am – 6.00 pm
Saturday: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sunday & PH: CLOSED
Monday – Friday: 9.00am – 6.00 pm
Saturday: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sunday & PH: CLOSED
Get Started
Recovery time varies, but most patients can expect full recovery within 6 to 12 months, depending on the severity of the fracture and adherence to physical therapy.
Most patients can return to normal activities with proper rehabilitation, though high-impact activities may need to be avoided, depending on the injury’s severity.
Most patients recover fully; however, some may experience long-term effects such as occasional pain or stiffness, especially if arthritis develops at the fracture site.