SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT WITH US
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic specialist for a detailed consultation & personalised treatment plan today.
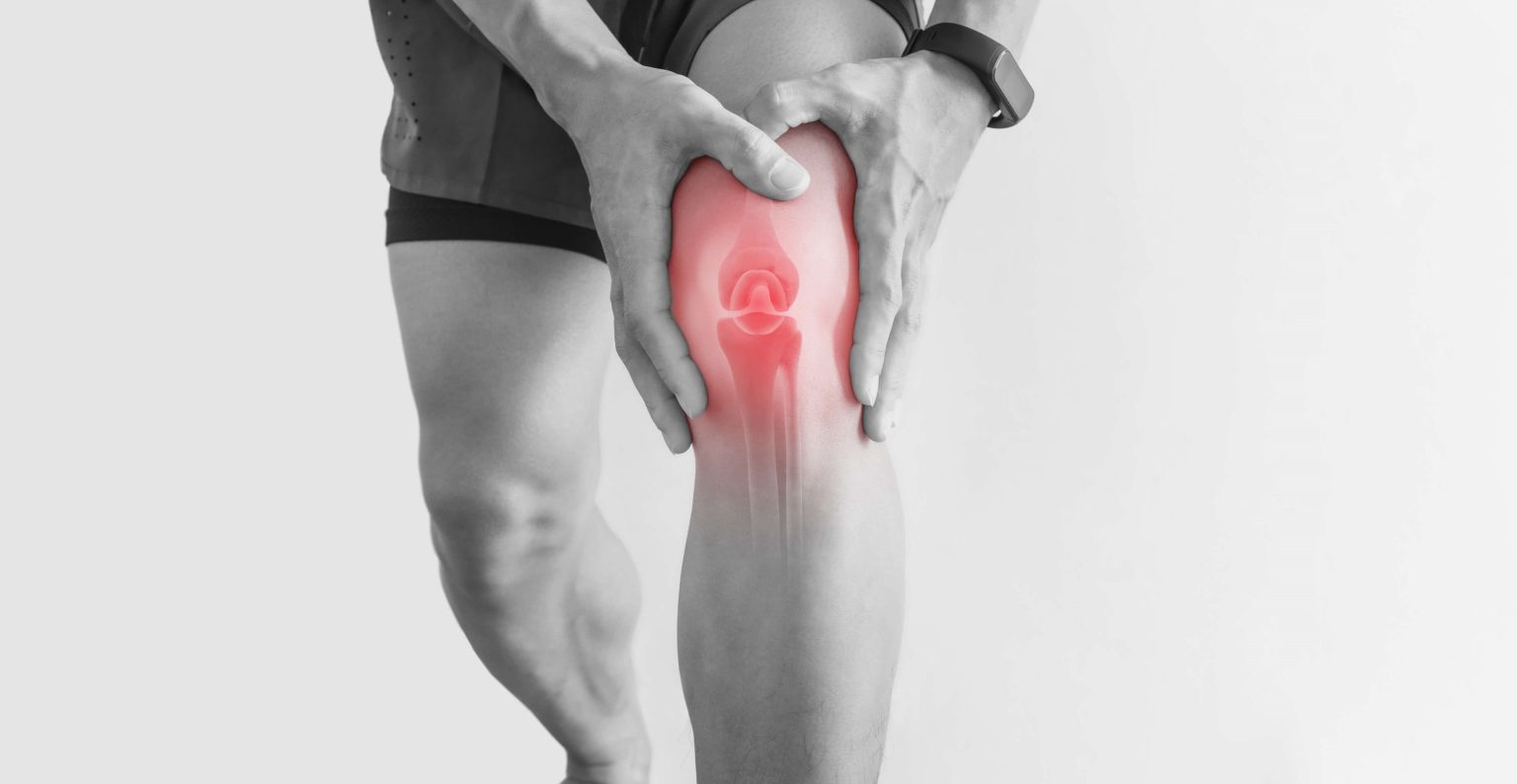
A knee cartilage injury occurs when the soft, cushioning tissue inside the knee joint is damaged. This damage can cause the cartilage to break down or tear, leading to difficulty in knee movement.
Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Knee cartilage injuries are fairly common and can happen to people of all ages, particularly those active in sports or with physically demanding jobs.
Knee cartilage injuries can occur during high-impact sports and activities. Several factors can increase this risk:
The symptoms of a knee cartilage injury can vary depending on the severity of the damage. Common signs include:
To accurately diagnose knee cartilage injuries, a combination of methods are used to confirm their presence and rule out other knee problems.
SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT WITH US
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic specialist for a detailed consultation & personalised treatment plan today.
Non-surgical treatments can help manage pain and improve knee function, while supporting the healing process. Here are some common non-surgical options:
Surgery for knee cartilage injuries is considered when the damage is significant and other treatments have failed. It aims to repair or replace damaged cartilage, restore knee function and reduce pain.
Revision knee arthroplasty is performed when a previous knee replacement is no longer functioning properly due to wear, infection, or mechanical issues. The surgeon removes the old implant and replaces it with a new one.
Partial knee replacement involves replacing only the damaged part of the knee while keeping the healthy areas untouched. This procedure typically results in a quicker recovery and more natural knee movement compared to a total knee replacement.
This procedure uses smaller incisions to repair or replace parts of the knee. This usually causes less pain and allows for a faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help lower the risk of knee cartilage injuries. Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling strengthen the muscles around the knee without stressing the cartilage. Wearing proper footwear during activities also supports the knees and reduces the risk of injury. Regular check-ups, particularly for individuals with a history of knee issues, can help in early detection and management of further knee damage.
Monday – Friday: 9.00am – 6.00 pm
Saturday: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sunday & PH: CLOSED
Monday – Friday: 9.00am – 6.00 pm
Saturday: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sunday & PH: CLOSED
Get Started
Recovery time depends on the type of surgery and the severity of the injury. Patients should avoid putting weight on the affected knee for a few weeks and follow a physical therapy programme for 3 to 6 months to get back to full knee movement.
Cartilage typically does not heal well on its own due to limited blood flow. Small injuries may improve with rest, but larger injuries often require surgery.
Yes, you can usually return to sports or exercise after surgery, depending on your recovery progress. It is recommended to begin with gentle activities before gradually progressing to more intense ones.